税收
在新加坡成为税务居民代表什么?
你可知道?在新加坡赚取的所有收入均需纳税。
您是特定课税年度的税务居民如果您是:
新加坡公民/新加坡永久居民
-
通常居住在新加坡的人除了临时缺席
在新加坡居住/工作的外国人
-
在上一个日历年至少 183 天;或者
-
连续连续3年
在新加坡工作过的外国人
-
跨越 2 个日历年的连续期间,并且您的总居留时间*至少为 183 天。
*包括您在受雇之前和之后的实际存在。
持有有效期至少一年的工作准证的外国人也将被视为税务居民。但是,当您根据税务居民规则终止工作时,您的税务居民身份将在清税时进行审查。如果您在新加坡逗留少于 183 天,您将被视为非居民。
在IRAS 网站上阅读更多信息。
新加坡的整体税收结构
税收帮助新加坡的发展以成为一个更强大的社区、更好的环境和更有活力的经济。税收用于资助政府支出。在 2020/21 财年��,构成政府运营支出的最大部门是社会发展部门。
Government Operating Expenditure 2023
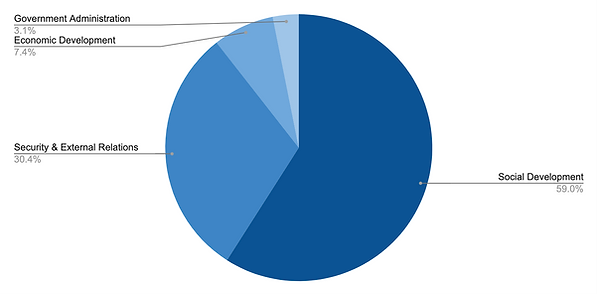
资料来源:Economic Survey of Singapore, Second Quarter 2021
所得税
税收被用来将新加坡发展成为一个更强大的社区、更好的环境和更有活力的经济。税收用于资助政府支出��。在 2020/21 财年,构成政府运营支出的最大部门是社会发展部门。


费率(居民)
费率(非居民)
就业收入税
非居民的就业收入按 15% 的统一税率或累进居民税率(见上表)征税,以较高税额为准。
董事费、咨询费和所有其他收入的税收
非居民个人的税率目前为 22%。它适用于所有收入,包括财产租金收入、养老金和董事费,但就业收入和某些按降低的预扣税率征税的收入除外。
您还可以使用非居民个人税款计算器 (XLS, 91KB) 来估算您的应付税款。
公司所得税
贵公司按其应课税收入的 17% 统一税率征税。这适用于本地和外国公司
政府向公司提供回扣,以降低其业务成本并支持其重组。
请参阅 IRAS 网站了解更多信息。
商品及服务税
GST 是一种消费税。当钱花在商品或服务(包括进口)上时,就要缴纳税款。自 2007 年起,新加坡征收 7% 的商品及服务税。
2023 年 1 月 1 日之后,购买商品和服务需缴纳 8% 的商品及服务税。
财产税
年度财产税的计算方法是将财产的年价值 (AV) 乘以适用于您的财产税率。建筑物的 AV 是出租物业的估计年租金总额,不包括家具、陈设和维护费。它是根据类似或可比较物业的估计市场租金而不是实际收到的租金收入来确定的。
商业和工业建筑和土地等非住宅物业按年价值的 10% 征税。自住业主税率不适用于非住宅物业,即使您购买的物业是供自己使用/占用的。
您在出租房产时收到的任何租金均需缴纳所得税,并且必须在您的所得税申报表中申报。
有关详细信息,请参阅IRAS’ 网站。
自住业主税率(住宅物业)

.png)
.png)
非自住住宅税率(住宅物业)

.png)
.png)
印花税
GST 是一种消费税。当钱花在商品或服务(包括进口)上时,就要缴纳税款。自 2007 年起,新加坡征收 7% 的商品及服务税。 2023 年 1 月 1 日之后,购买商品和服务需缴纳 8% 的商品及服务税。
Restrictions
买方印花税 (BSD)
您需要为转让或买卖位于新加坡的财产而签署的文件支付 BSD。 BSD 将根据要加盖印花的文件中所述的购买价格或房产的市场价值(以较高金额为准)计算。
当房产更贵时,你的税率就会更高。目前,住宅物业的前 180,000 新币税率为 1%;接下来的 180,000 新币为 2%,接下来的 640,000 新币为 3%;剩余金额的 4%。
在此处阅读有关 BSD 的更多信息。
Restrictions
Additional Buyer's Stamp Duty (ABSD)
附加买家印花税是 BSD 之上的另一种税。但是,它仅适用于新加坡永久居民和外国人,或打算在新加坡购买不止一处住宅的新加坡公民。
除非您是冰岛、列支敦士登、瑞士或美国的公民或永久居民,否则您需要为购买的每处房产额外支付 20%。
除了买方印花税 (BSD) 之外,买家还需要支付额外的买方印花税 (ABSD)。 ABSD 费率因外国人和永久居民而异。
对于外国人,购买任何住宅物业都需要支付购买价格或物业市场价值 30% 的 ABSD,以较高者为准。
同时,对于 PR,购买您的第一、第二和第三住宅物业分别需要 5%、25% 和 30%。
假设您有一个住宅物业,一个公寓。价格为100万新元。
外国人购买任何住宅物业都将产生 30% 的 ABSD。
30100 1,000,000 新币 = 300,000 新币
同时,永久居民购买他们的第一个住宅物业需要支付 5% 的 ABSD。
5100 1,000,000 新币 = 50,000 新币
差额高达25万新币!
机动车税
这些是对机动车辆征收的除进口税以外的税种。征收这些税是为了遏制汽车拥有量和道路拥堵。
Restrictions
索取进项税
机动车
根据消费税(一般)条例第 27 条,汽车的成本和运行费用(除了 1998 年 4 月 1 日之前签发的带有 COE 的 Q 牌汽车外)是不允许的费用。因此,汽车的购买和运行费用(例如汽油和停车费用)所产生的消费税不可申请退税。
其他机动车辆
对于不属于“机动车”定义的其他机动车辆(例如卡车、厢式货车和摩托车),购买机动车辆和运行费用所产生的消费税可抵扣,但须符合进项税的条件宣称。
Restrictions
销售征收销项税
如果您不是机动车经销商,当您偶尔出售在您的业务中使用过的车辆时,您应该使用折扣销售价格计划。在此计划下,您在出售二手车时需要按售价的 50% 征收消费税。
遗产税
遗产税是对一个人在其去世时的全部资产(包括现金和非现金资产)的市场价值征收的税款。无论这个人是否拥有遗嘱,其资产仍然需要缴纳遗产税。遗产税在2008年2月15日及以后的去世情况下已经被取消。
逝者的全部财产被称为遗产。对于大多数遗产而言,由于提供了各种豁免条款,不需要支付遗产税。
一个人的遗产包括:
-
他或她以个人名义拥有的一切
-
逝者与他人共同拥有的财产份额
-
在逝者去世前五年内所作的礼物
-
任何时间所作的礼物,但逝者仍保留某些权益(例如,即使房子在10年前转让给他人,但逝者仍然可以收取每月的租金收入)
-
由他或她作为受益人从信托中获得某些个人利益的资产(例如,为尚未成年的子女设立的信托银行账户)
遗产税适用的常见资产
-
不动产
-
新加坡以外的不动产在新加坡不受遗产税的征税对象。
-
银行账户
-
上市股票
-
保险箱中的物品
请参考新加坡税务局IRAS’ 网站获取更多信息
其他税款
以下是新加坡存在的其他未提及的税款:
Restrictions
外籍劳工费
如果您雇佣工作准证持有人,您将需要为每名员工支付每月的劳工费。
外籍劳工费,通常称为“劳工费”,是一种定价机制,用于调控新加坡的外国人数量。
您必须为工作准证持有人支付每月的劳工费。劳工费的支付责任始于临时工作准证或工作准证签发的当天,以较早者为准。当准证被取消或到期时,支付责任终止。
劳工费率和配额
您支付的劳工费通常取决于以下两个因素:
-
工人的资格。
-
雇佣的工作准证或技⼯签证持有者的数量。
请参考新加坡劳动部 Ministry of Manpower (MOM) 的网站获取更多信息。
Restrictions
水税
月度账单中水费由三个组成部分构成:水费、水资源保护税和水运费。
水费
水费涵盖了水生产过程中各个阶段所产生的费用,包括雨水收集、原水处理以及通过广泛的全岛水管网络向客户提供处理后的饮用水。水费根据消耗的水量收取。
水资源保护税
水资源保护税(WCT)于1991年引入,旨在鼓励节水行为并反映水的稀缺价值。水资源保护税按水费的百分比征收,以强调水是宝贵的,每一滴水都应珍惜。
水运费
每一滴使用过的水都通过独立的下水道网络收集,并输送到水再生厂进行处理,然后进一步净化为NEWater或排入海中。
The Waterborne Fee (WBF) goes towards meeting the cost of treating used water and maintaining the used water network. It is charged based on the volume of water usage.
For further information on Domestic Households Water Prices, visit the PUB website here.
Tax Exemption Schemes for Start-Ups
The tax exemption scheme for new start-up companies and partial tax exemption scheme for companies are tax reliefs available to reduce companies’ tax bills.
The tax exemptions for qualifying companies for their first 3 consecutive YAs are as follows:
-
75% exemption on the first $100,000 of normal chargeable income*; and
-
A further 50% exemption on the next $100,000 of normal chargeable income*.
* Normal chargeable income refers to income to be taxed at the prevailing Corporate Income Tax rate of 17%.
Tax Exemption on First $200,000 of Chargeable Income
_edited.jpg)
The maximum exemption for each YA is $125,000 ($75,000 + $50,000).
Qualifying Conditions for Tax Exemption Scheme for New Start-Up Companies
All new start-up companies are eligible for the tax exemption scheme, except:
-
Companies whose principal activity are that of investment holding
-
Companies that undertake property development for sale, investment, or both
The new start-up company must also:
-
Be incorporated in Singapore
-
Be a tax resident of Singapore for that YA
-
Have its total share capital beneficially held directly by no more than 20 shareholders throughout the basis period for that YA where:
-
All the shareholders are individuals; or
-
At least 1 shareholder is an individual holding at least 10% of the issued ordinary shares of the company
-
Tax Concessions for Royalty
Royalty is earned in Singapore if it is:
-
paid directly or indirectly by a person resident in Singapore or by a permanent establishment in Singapore; or
-
deductible against any income earned in or derived from Singapore.
Qualifying for tax concession
To qualify for the tax concession, the royalties must be received for:
-
any literary, dramatic, musical or artistic work; or
-
approved intellectual property or approved innovation.
If you qualify, you will be taxed on the lower of:
-
amount of royalties after allowable deductions; or
-
10% of the gross royalties.
The tax concession does not apply to royalties received for any work published in:
-
any newspaper;
-
periodical;
-
approved intellectual property or innovation (from Year of Assessment 2017).
Life Insurance Relief
You may claim Life Insurance Relief for the Year of Assessment 2022 if you satisfy all these conditions:
1. Your total contributions for the following in 2021 was less than $5,000;
a. compulsory employee CPF contribution;
b. self-employed Medisave/voluntary CPF contribution; and
c. voluntary cash contribution to your Medisave account.
2. You paid insurance premiums in 2021 on your own life* insurance policy; and
3. The insurance company must have an office or branch in Singapore if your policies are taken on or after 10 August 1973.
As long as the individual (SC/PR/Foreigner) is a tax resident in Singapore and meets the qualifying conditions, he can claim tax reliefs, including the life insurance relief.
Supplementary Retirement Scheme
(SRS)
The Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS) is a voluntary scheme to encourage individuals to save for retirement, over and above their CPF savings.
Contributions to SRS are eligible for tax relief.
Investment returns are tax-free before withdrawal and only 50% of the withdrawals from SRS are taxable at retirement.
Singapore Citizens, Singapore Permanent Residents (SPRs) and foreigners who derive any form of income may make SRS contributions in the current year. You must be:
-
At least 18 years of age;
-
Not an undischarged bankrupt;
-
Not having a mental disorder; and
-
Capable of managing yourself and your affairs.
You and/or your employer (on your behalf) may contribute at any time, and as often as you like, subject to the maximum SRS contribution for the year. Contributions must be made in cash.
You may withdraw funds from your SRS account any time. Withdrawals can be made:
-
- in cash;
-
- in the form of investments for the qualifying types of withdrawal.
Withdrawals in the form of monies or investment from your SRS Account are subject to income tax and added to your other taxable income (e.g. employment, rental).
When a foreigner or Singapore Permanent Resident withdraws from his SRS account, the withdrawal is subject to withholding tax.
Parenthood Tax Rebate
Married, divorced or widowed parents may claim tax rebates of up to $20,000 per child.
As PTR is a one-off rebate, you may only claim PTR on a qualifying child once.
Qualifying for rebate
PTR is given to tax residents to encourage them to have more children.
To qualify, you must be a Singapore tax resident who is married, divorced or widowed in the relevant year.
You may use the PTR Eligibility Tool (XLSM, 52KB) to check your eligibility for PTR.
Amount of rebate
You and your spouse may share the PTR based on an apportionment agreed by both of you. If your percentage of PTR claimed does not add up to 100% or you are unable to agree on the apportionment, we will apportion the PTR equally between the both of you.
Child Order | PTR (For child born from 2008 onwards) |
|---|---|
1st
2nd
3rd
5th child and subsequent
4th
$10,000
$20,000
$20,000
$20,000 per child
$5,000
Earned Income Relief
Earned Income Relief is for individuals who are gainfully employed or carrying on a trade, business, profession or vocation.
Qualifying for relief
You will receive Earned Income Relief if you have taxable earned income from any of the following sources in the previous year:
Amount of relief
The amount of Earned Income Relief is based on your age and taxable earned income (less any allowable expenses) in the previous year.

* If the amount of taxable earned income is lower than the maximum amount claimable, the relief will be capped at the amount of taxable earned income.
For example, if you are 55 years old as at 31 Dec 2021 and have taxable earned income of $5,000 in 2021, you will get Earned Income Relief of $5,000 (instead of $6,000) for the Year of Assessment 2022.
Spouse Relief/
Handicapped Spouse Relief
Qualifying for relief
You may claim Spouse Relief in the Year of Assessment 2023 if you have supported your spouse and satisfy all these conditions in 2022:

Legally separated spouses
If you are legally separated from your wife, you may claim this relief if you have made maintenance payments under a Court Order or Deed of Separation.
Divorced spouses
Divorced taxpayers who pay alimony to their former spouses are not eligible to claim this relief.
Amount of relief

Central Provident Fund(CPF)
Relief for employees
CPF Relief is given to encourage individuals to save for their retirement. Employees who are Singapore Citizens or Singapore Permanent Residents may claim CPF Relief. To understand more about CPF, please refer to Access to CPF.
Amount of relief
CPF Relief is capped by the amount of compulsory employee CPF contributions made on Ordinary Wages and Additional Wages under the CPF Act.
The amount of CPF Relief is capped to ensure that CPF is not used as a tax shelter.
You may claim CPF Relief for making employee CPF contributions on wages that have not exceeded the Ordinary Wage ceiling and Additional Wage ceiling.
For more information on OW ceiling and AW ceiling, please refer to CPF Board's website.
Family Tax Office Structure
The concept of a ‘family office’ does not have a fixed definition. Typically, it is conceptualised as an entity which provides a variety of services that a family may need.
-
The new conditions explicitly require a minimum fund size of S$10 million at the point of application and the fund must commit to increase its AUM to S$20 million within a two-year grace period.
-
The minimum fund size for Section 13U Tax Incentive Scheme (s13U Scheme) remains unchanged at S$50 million at the point of application.
s13O Scheme –
Currently, the s13O Scheme only required the fund to be managed or advised directly by a fund management company (FMC) in Singapore, where the FMC holds a capital markets services licence pursuant to the Securities and Futures Act 2001 (SFA) or is exempt from the requirement to hold such a licence under the SFA.
From 18 April 2022, the fund must now be managed or advised directly throughout each year by a family office in Singapore, where the family office employs at least two Investment Professionals. An Investment Professional includes:
-
portfolio managers;
-
research analysts; and
-
traders;
-
who are earning more than S$3,500 per month; and
-
must be engaging substantially in the qualifying activity.
If the family office is unable to employ two Investment Professionals at the point of application, the fund is given a one-year grace period to employ the second Investment Professional.
s13U Scheme – The fund must also be managed or advised directly throughout the year by a family office in Singapore, where the family office employs at least three Investment Professionals. More importantly, one of the three Investment Professionals must be a non-family member of the beneficial owner(s). The same definition of “family” discussed above is applied here as well. If the family office is unable to employ one non-family member as an Investment Professional at the point of application, the fund is given a one-year grace period to do so.
It should be noted that Investment Professionals must be tax resident in Singapore.
Donations and Tax Deductions
Fun fact: Did you know? In Singapore, for every $1 you donate to the Community Chest or any IPC, $2.50 will be deducted from your taxable income for the year!
Donate to Community Chest or any approved Institution of a Public Character (IPC) before the year ends, and enjoy tax deductions of 2.5 times the qualifying donation amount next tax season.
-
Cash Donations
-
Shares Donations
-
Computer Donations
-
Artefact Donations
-
Donations under the Public Art Tax Incentive Scheme (PATIS)
-
Land and Building Donations
For more information on donations and tax deductions, please refer to IRAS’ website.
https://www.iras.gov.sg/taxes/other-taxes/charities/donations-tax-deductions
Compulsory Medisave Contributions
Compulsory Medisave Contributions
You must make compulsory contributions to your Medisave Account after you receive a Notice of Computation (NOC) of CPF Contributions from IRAS if:
-
You are a self-employed person;
-
You are a Singapore Citizen or Permanent Resident; and
-
Your net trade income# is more than $6,000.
#Net trade income is your gross trade income minus all allowable business expenses, capital allowances and trade losses.
Amount of Compulsory Medisave Contributions
The Medisave amount that you have to contribute yearly depends on your:
-
age;
-
income level; and
-
net trade income for the previous year.
The Medisave contribution amount is generally a percentage of your total business trade income subject to a maximum cap.
Medisave Contribution Rates for Year 2017
Age as at 1 Jan 2017
Yearly Net Trade Income
Example: 37 year-old with net trade income of $65,000 in 2017
Age as at 1 Jan 2017
37 years old
Net Trade Income in 2017
$65,000
Medisave Contribution Rate:
9%
Maximum Cap for Age Group
$6,480
Amount of Medisave Contribution Payable
$5,850
Lower of $6,480 or (9% x $65,000)
For more Medisave contribution rates, please refer to the CPF Board website.
Voluntary Contributions to Medisave Account (VC-MA)
You may also make voluntary contributions to your Medisave account and claim tax reliefs to lower your taxes.
Tax Relief for Voluntary Contributions
You may claim tax relief for your voluntary Medisave contributions if:
-
You are a Singapore Citizen or Permanent Resident;
-
You have made voluntary contributions to your Medisave account in the previous year; and
-
You derived any source of income (e.g. from rental, director's fees, etc.) in the year you made the voluntary contributions.
Avoidance of Double Taxation Agreement (DTA)
Juridical double taxation results when the same income is being taxed twice - once in the jurisdiction where the income arises and another time in the jurisdiction where the income is received.
Juridical double taxation results when the same income is being taxed twice - once in the jurisdiction where the income arises and another time in the jurisdiction where the income is received.
Jurisdictions enter into DTAs to mitigate the effects of double taxation. A DTA partner refers to a jurisdiction which has signed a DTA with Singapore.
Only the tax residents of Singapore and the respective DTA partner can enjoy the benefits of a DTA.
Benefits Under DTAs
Depending on the provisions of the DTA, you may claim the benefits of an exemption from the tax on income for personal services, teachers, researchers, artistes, athletes, students, trainees, etc.
Tax Residents of DTA Partners
If you are a tax resident of a jurisdiction that has concluded a DTA with Singapore, you may be protected from being taxed twice on the same income in Singapore.
Singapore has signed Avoidance of Double Taxation Agreements (“DTAs”), limited DTAs and Exchange of Information Arrangements (“EOI Arrangements”) with around 100 jurisdictions.
You can find the list of jurisdictions here.
Singapore has no Capital Gains Tax
Non-taxable gains from sale of property, shares and financial instruments
The following gains are generally not taxable:
-
Gains derived from the sale of a property/fixed assets in Singapore as it is a capital gain.
-
Profits or losses derived from the buying and selling of shares or other financial instruments are viewed as personal investments (capital transactions on foreign exchange)
-
Payouts from insurance policies as they are capital receipts.
Taxable gains from sale of property
The gains may be taxable if you buy and sell property with a profit-seeking motive or deemed to be trading in properties.
Some criteria used to assess if you are trading in properties are as follows:
-
- Frequency of transactions (buying and selling of properties);
-
- Reasons for buying and selling of property;
-
- Financial means to hold the property for long term; and
-
- Holding period.
Reporting gains from sale of property
You must declare taxable gains from the sale of property under 'Other Income' in your Income Tax Return. If you are unsure whether your gains from sale of property are taxable, please email us.
You do not need to declare gains that are not taxable in your Income Tax Return.
Enhanced Tier Fund Exemption Scheme (ETF Scheme)
The ETF Scheme has a number of qualifying conditions and requires the approval of the MAS.
The qualifying conditions include:
• the fund must have a minimum fund size of S$50 million at the time of application;
• the fund must be managed or advised by the relevant family office;
• the family office must employ at least 3 resident investment professionals in Singapore who are substantively engaged in an investment management or advisory role; and
• the fund must incur at least S$200,000 in business spending in Singapore.
The ETF Scheme has been extended to all forms of fund vehicles, including a Singapore VCC.
Approval under the ETF Scheme is ultimately at the discretion of the MAS and therefore cannot be guaranteed even if all qualifying conditions are satisfied.
The ETF Scheme is generally granted to a fund entity upon an application being approved by MAS. Once granted, exemption will take effect from the date of application and available for the life of the IHC fund (based on the terms of the approval).
Tax exemption applies to all specified income from designated investments as the terms are defined for the purposes of the tax exemption.
There are however many different ways to structure the family office and the fund entity(ies).
Singapore Resident Fund Scheme
The Singapore Resident Fund Scheme was introduced to encourage fund managers to base their fund vehicles in Singapore, by giving Singapore based funds the same tax exemptions given under the offshore fund regime (e.g. to a Cayman Islands fund).
Successful applicants under the 13R and 13X schemes will be granted employment passes (one for 13R and three for 13X), which can offer an interim solution pending permanent residency applications.
13R and 13X funds that are approved for the tax incentive scheme before 31 December 2024 can enjoy the benefits of the scheme for the life of the fund, provided that the on-going operational conditions for the entities are met.
Family offices set up under the 13R and 13X scheme can also utilise the new Variable Capital Company (VCC) structure. A VCC can be set up as a standalone fund, or as an umbrella fund with two or more sub-funds. A VCC structure is regarded as a single company, with a single identity for tax purposes, removing the need for multiple tax returns.
Shares of a VCC are redeemable at the fund’s net asset value (NAV), and VCCs can pay dividends from the capital, which is not typically allowable in other forms of corporate vehicles. In addition, VCC shareholders register will not be publicly available, offering privacy to investors.
Information is from Sovereign Group and PWC
Requirements:
-
Company must be incorporated and tax resident in Singapore
-
S$200,000 in expenses per annum
-
No minimum fund size requirement
Non-qualifying investors are subject to a financial penalty, which is the percentage held by the beneficial owner in the fund x the amount of income derived by the fund x the income tax rate applicable to the fund had the income not be en exempt (i.e., 17% for a company)
Annual declarations to MAS required Annual statements to investors required Declaration to IRAS required if financial penalty applies. Tax returns and corporate filings required (the MAS has informally clarified that new changes may be implemented to allow annual statements to be issued to only non-qualifying investors)
Information is from EDB











